In this post, I link to and excerpt from the 2019 ACC/AHA Guideline on the Primary
Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease [PubMed Abstract] [Full-Text HTML] [Full-Text PDF]. Circulation. 2019 Sep 10;140(11):e596-e646. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000678. Epub 2019 Mar 17.
All that follows is from the above resource.
Jump to
- Table of Contents
- Top 10 Take-Home Messages for the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease
- Preamble
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Overarching Recommendations for ASCVD Prevention Efforts
- 3. Lifestyle Factors Affecting Cardiovascular Risk
- 4. Other Factors Affecting Cardiovascular Risk
- 5. Cost and Value Considerations
- 6. Conclusion
- ACC/AHA Task Force Members
- Presidents and Staff
- Footnotes
- References
- Supplemental Material
TOP 10 TAKE-HOME MESSAGES FOR THE PRIMARY PREVENTION OF CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE
1. The most important way to prevent atherosclerotic
vascular disease, heart failure, and atrial fibrillation
is to promote a healthy lifestyle throughout life.
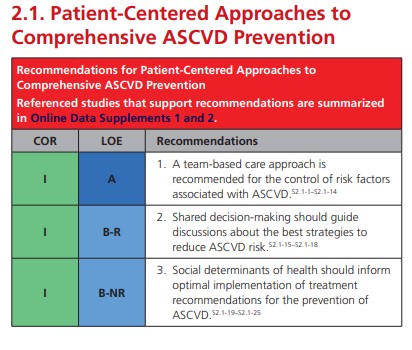
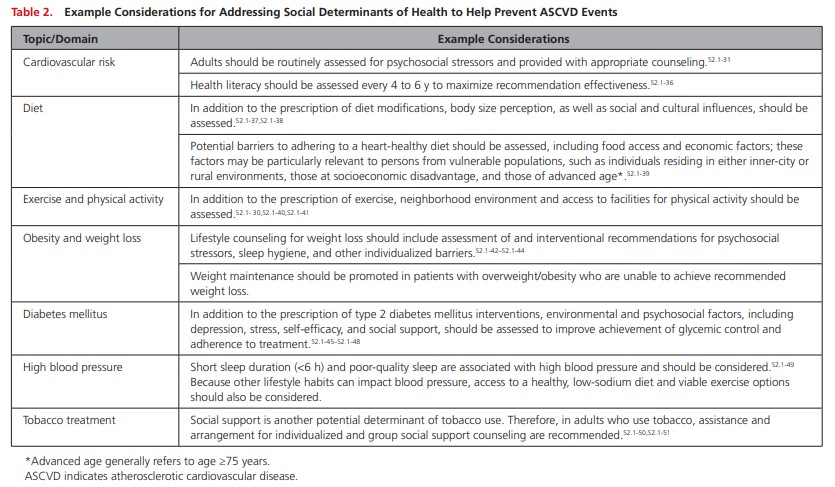
2. A team-based care approach is an effective strategy for the prevention of cardiovascular disease. Clinicians should evaluate the social determinants of health that affect individuals to inform treatment decisions.
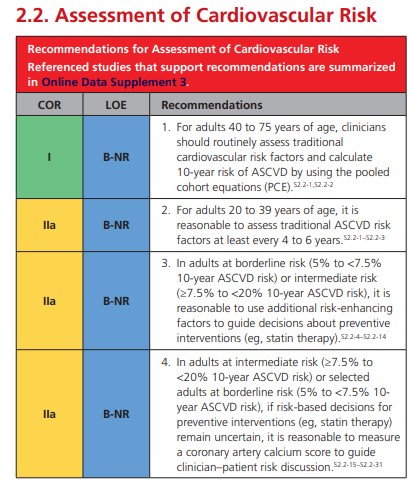
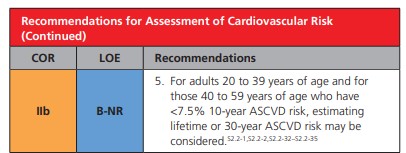
3. Adults who are 40 to 75 years of age and are being
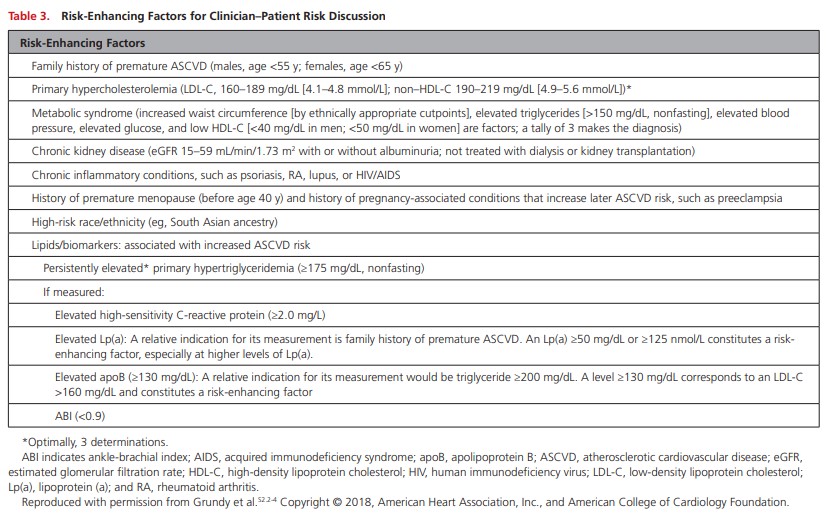
evaluated for cardiovascular disease prevention should undergo 10-year atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk estimation and have a clinician–patient risk discussion before starting on pharmacological therapy, such as antihypertensive therapy, a statin, or aspirin. In addition, assessing for other risk-enhancing factors can help guide decisions about preventive interventions in select individuals, as can coronary artery calcium scanning.
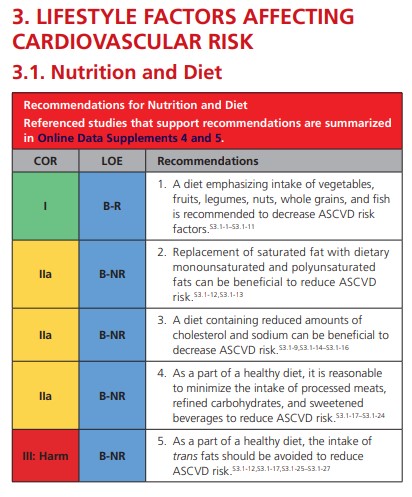
4. All adults should consume a healthy diet that emphasizes the intake of vegetables, fruits, nuts, whole grains, lean vegetable or animal protein, and fish and minimizes the intake of trans fats, red meat and processed red meats, refined carbohydrates, and sweetened beverages. For adults with overweight and obesity, counseling and caloric restriction are recommended for achieving and maintaining weight loss.
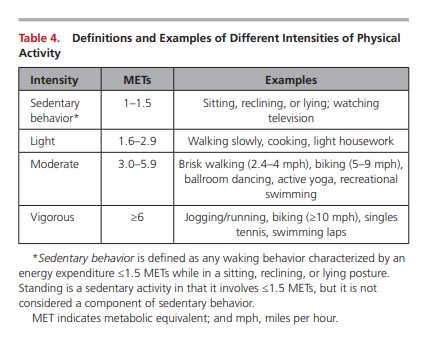
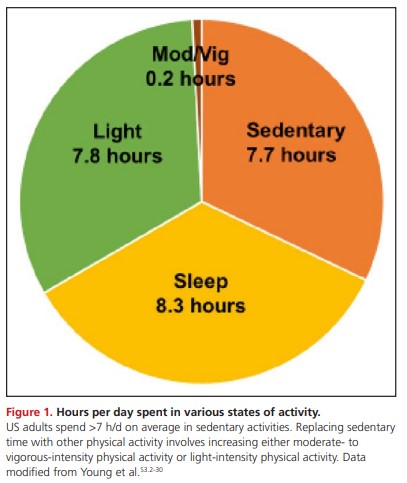
5. Adults should engage in at least 150 minutes per week of accumulated moderate-intensity physical activity or 75 minutes per week of vigorous-intensity physical activity.
6. For adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus, lifestyle changes, such as improving dietary habits and achieving exercise recommendations, are crucial. If medication is indicated, metformin is first-line therapy, followed by consideration of a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor or a glucagonlike peptide-1 receptor agonist.
7. All adults should be assessed at every healthcare visit for tobacco use, and those who use tobacco should be assisted and strongly advised to quit.
8. Aspirin should be used infrequently in the routine primary prevention of ASCVD because of lack of net benefit.
9. Statin therapy is first-line treatment for primary
prevention of ASCVD in patients with elevated low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels (≥190 mg/dL), those with diabetes mellitus, who are 40 to 75 years of age, and those determined to be at sufficient ASCVD risk after a clinician–patient risk
discussion.
10. Nonpharmacological interventions are recommended for all adults with elevated blood pressure or hypertension. For those requiring pharmacological therapy, the target blood pressure should generally be <130/80 mm Hg.—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
Start at e612 box