Today, I review, link to, and embed “CKD Staging (Cr vs. Cystatin C, Albuminuria & more): Mind The Gap Segment” From CoreIM. Posted: November 8, 2023
By: Dr. Cary Blum, Dr. Shreya P. Trivedi, Dr. Yichi Zhang and Dr. Greg Katz
Graphic: Ariella Coler-Reilly
Audio: Yichi Zhang.
All that follows is from the above resource.
Podcast: Play in new window | Download
Time Stamps
- 00:13 Reviewing CKD Classification!
- 04:20 What’s wrong with how we estimate GFR?
- 06:50 Why is creatinine flawed as an estimator of GFR?
- 10:52 Enter new contender…Cystatin C!
- 16:16 Importance of the A Stage!
- 20:21 Which patients should you measure proteinuria in?
- 22:10 Treatments for albuminuria!
- 24:27 Summary and Closing
CME-MOC
- Get CME-MOC credit with ACP!
Sponsor:
Panacea Financial Student Loan Consultation
Get all your student loan, tax questions and public loan forgiveness questions answered from the Student Loan Consultation service. $200 flat fee and have access to that certified student loan professional AFTER your consultation.
Panacea Financial provides banking built for doctors, by doctors.Panacea Financial is a division of Primis, Member FDIC. Panacea partners with TCG advisors to provide student loan consultations
Show Notes
Welcome to the “Stage”: GFR and Albuminuria
Reviewing CKD Classification!
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) introduced a dual-staging criteria for chronic kidney disease (CKD)
- eGFR Staging (G-Stage)
- eGFR between 60 – 120 ml/min/1.73 m2
- NOT clinically significant CKD
- Stage G3
- Stage G3a
- 45 < eGFR < 59
- Stage G3b
- 30 < eGFR < 44
- Stage G4
- 15 < eGFR < 29
- Stage G5
- eGFR < 15
- Albuminuria (A-Stage)
- Measured by albumin-to-creatinine ratio (ACR) in mg/g.
- The gold standard definition for staging albuminuria involves checking 24 hour albumin excretion.
- However, in practice, we make the assumption that all human excrete 1g of creatinine per 24 hours and this allows us to check a spot urine test
- Stage A1
- 0 < ACR < 30 mg/g
- Stage A2
- 30 < ACR < 300 mg/g
- Moderately elevated (previously “microalbuminuria”)
- Stage A3
- > 300 mg/g ACR
- Severely elevated (previously “macroalbuminuria”)
- Both the G-stage and A-stage are independent risk factors for cardiovascular and renal events!
What’s WRONG with how we estimate GFR?
- The ideal molecule to estimate GFR does NOT exist!
- Ideal Qualities:
- Exact serum quantity is known
- Freely filtered at glomerulus
- Neither secreted NOR reabsorbed in the tubules
- Ex: Insulin used historically
- but cumbersome since requires injection
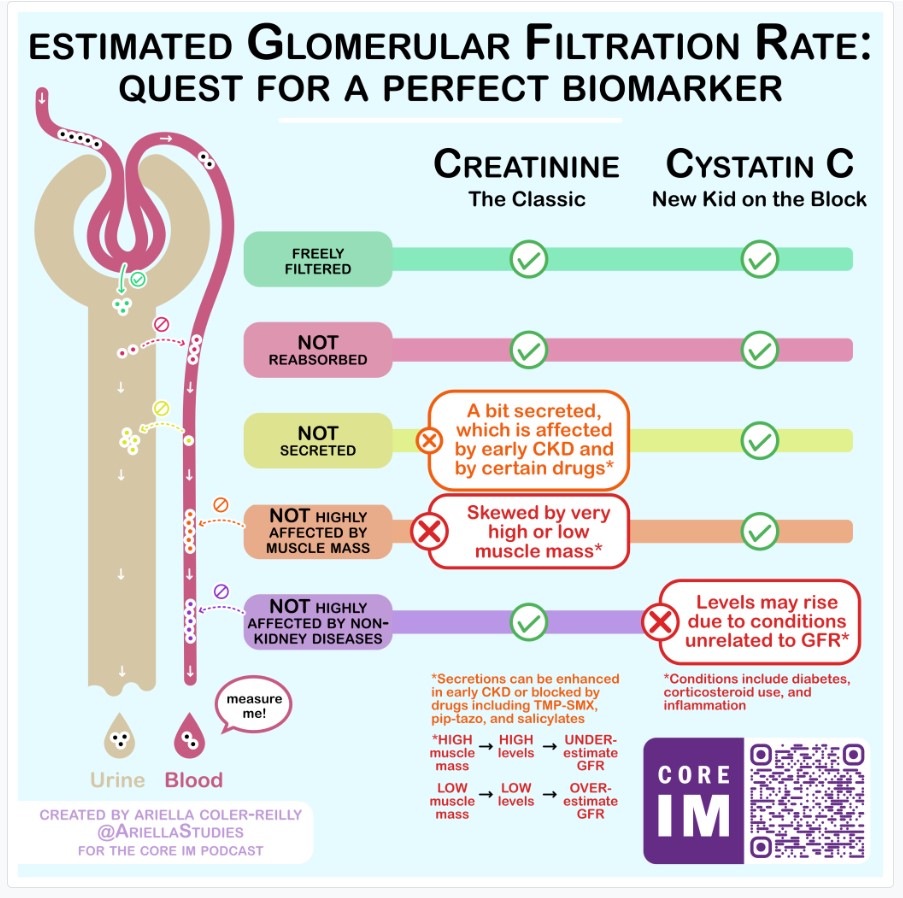
- Why is creatinine flawed as an estimator of GFR?
- Creatinine is used as an endogenous estimator
- Varies with muscle mass
- Differs between patients based on:
- Sex
- Age
- Low muscle mass → lower levels of creatinine
- Result: Cr will overestimate eGFR measurements & give false reassurance!
- Example: Cr of 1 mg/dl in a 90-year-old frail female
- Higher muscle mass → higher levels of creatinine
- Result: Cr will underestimate eGFR measurements
- Ex. Serum Cr of 1.8 mg/dL in Arnold Schwarzenegger or Shaq
- Actively secreted in the renal tubules
- Secretion rate is influenced by medications!
- Bactrim blocks secretion
- Creatinine secretion is enhanced in healthy “remnant” nephrons of mild to moderate CKD
- Race-adjusted eGFR formula
- African Americans were systematically under-staged (i.e., for a given creatinine, higher eGFR would be reported → undiagnosed CKD)
- Enter a NEW Contender: Cystatin C!
- Advantages
- Does not vary based on muscle mass
- Since it is made in every nucleated cell!
- Freely filtered in the glomerulus
- Neither secreted or reabsorbed in the renal tubules
- Disadvantages
- Affected by sex and age
- But, you can correct for these!
- Affected by inflammation and chronic diseases
- Diabetes
- Cigarette smoking
- Thyroid disease
- Cancer
- HIV
- Steroid use
- Which patient should I order Cystatin C for?!
- Patients with low muscle mass
- Who may be under staged by creatinine measurements alone
- Erroneously reporting higher eGFR
- Patients with high muscle mass
- Who may be falsely labeled with CKD
- From a creatinine derived eGFR
- Which marker of eGFR is the best?
Assessing Qualitative Renal Function using A-Stage! (Albuminuria)
- A Dive into the Endothelium!
- Endothelial dysfunction → Albuminuria
- Urine = Direct pathway to observe endothelial dysfunction
- Can start to occur well BEFORE any significant changes to GFR!
- A-Stage
- Helps identify patients who (1) are in early stages of renal dysfunction and (2) who can respond well to more aggressive interventions!
- Potential treatments:
- ACE-i/ARBs
- ONLY have renal-protective function in patients with albuminuria!
- Otherwise are just like other BP meds
- SGLT2i
- Shown to decrease decline in GFR, ESRD, and death
- DAPA-CKD trial Pro tip! If proteinuria is still > 500 mg/g with RAASi and SGLT2i, can consider adding finerenone!
- You can trend A-Stage to assess the effectiveness of treatment interventions!
- Make sure to measure albuminuria ESPECIALLY in patients with:
- Diabetes AND known CKD
- Confounding Factors for albuminuria
- The following activities can lead to spillage of albumin into urine! (not actual renal dysfunction) → transient albuminuria
- Exercise
- Standing upright
- Inflammation
- How do we measure A-Stage?
- Urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio (ACR)
- Most commonly used!
- Influenced by denominator (creatinine)
- Note: Urine albumin WITHOUT reporting urine creatinine is NOT meaningful!
- But this is affected by all the aforementioned flaws of creatinine measurement
- 24-hour urine albumin
- Gold standard!
- Can be quite cumbersome to collect/perform, especially in outpatient settings