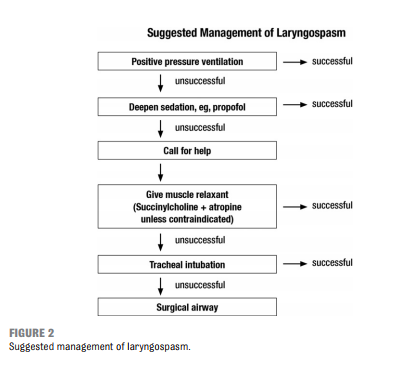
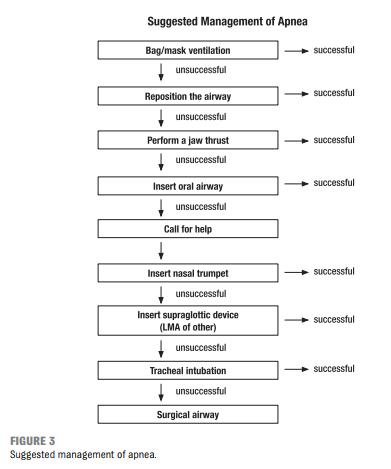
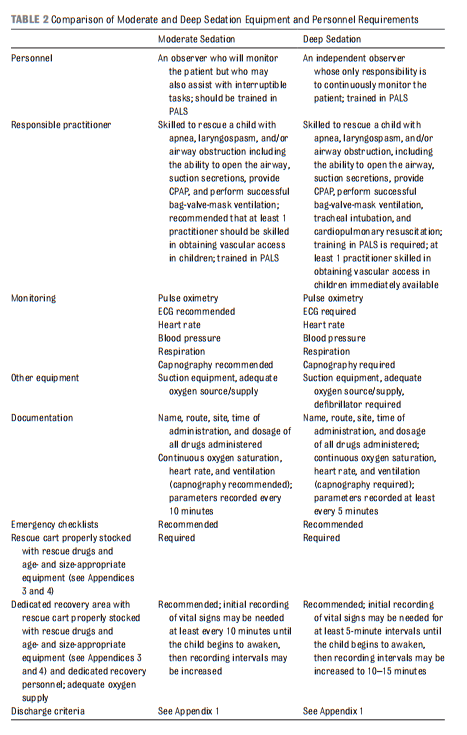
Resource (1), Guidelines for Monitoring and Management of Pediatric Patients Before, During, and After Sedation for Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures: Update 2016, is an outstanding resource on pediatric sedation worth reviewing often.
Because pediatric sedation emergencies are rare, routine use of pediatric sedation case simulation of emergencies is recommended in the resource.
The following are excerpts from Resource (1):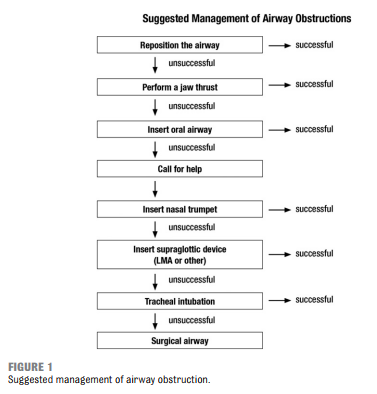
PREPARATION FOR SEDATION PROCEDURES
Part of the safety net of sedation is using a systematic approach so as to not overlook having an important drug, piece of equipment, or monitor immediately available at the time of a developing emergency. To avoid this problem, it is helpful to use an acronym that allows the same setup and checklist for every procedure. A commonly used acronym useful in planning and preparation for a procedure is SOAPME, which represents the following:
S = Size-appropriate suction catheters and a functioning suction apparatus (eg, Yankauer-type suction)
O = an adequate Oxygen supply and functioning flow meters or other devices to allow its delivery
A = size-appropriate Airway equipment (eg, bag-valve-mask or equivalent device [functioning]), nasopharyngeal and oropharyngeal airways, LMA, laryngoscope blades (checked and functioning), endotracheal tubes, stylets, face mask
P = Pharmacy: all the basic drugs needed to support life during anemergency, including antagonists as indicated
M = Monitors: functioning pulse oximeter with size-appropriate
oximeter probes, 361, 362 end-tidal carbon dioxide monitor, and other monitors as appropriate for the procedure (eg, noninvasive blood pressure, ECG, stethoscope)E = special Equipment or drugs for a particular case (eg, defibrillator)
See my post Local Anesthetic Agents And The Management OfLocal Anesthetic Sytemic Toxicity [pending].
Resources:
(1) Guidelines for Monitoring and Management of Pediatric Patients Before, During, and After Sedation for Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures: Update 2016 [PubMed Abstract] [Full Text HTML] [Full Text PDF]. Pediatrics. 2016 Jul;138(1). pii: e20161212. doi: 10.1542/peds.2016-1212.
(2) Supplemental Information for Resource (1) above. [PDF]
- APPENDIX 1: RECOMMENDED DISCHARGE CRITERIA
- APPENDIX 2: ASA PHYSICAL STATUS CLASSIFICATION*
- APPENDIX 3: DRUGS† THAT MAYBE NEEDED TO RESCUE A SEDATED
PATIENT - APPENDIX 4: EMERGENCY EQUIPMENT THAT MAY BE NEEDED
TO RESCUE A SEDATED PATIENT†, ‡
(3) Core Competencies for Pediatric Providers Who Deliver Deep Sedation from the Society For Pediatric Sedation.
(4) Pediatric laryngospasm [PubMed Abstract] [Full Text PDF]. Paediatr Anaesth. 2008 Apr;18(4):303-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9592.2008.02446.x.
(6) Physiologic monitoring practices during pediatric procedural sedation: a report from the Pediatric Sedation Research Consortium [PubMed Abstract] [Full Text HTML] [Full Text PDF available for download]. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2012 Nov;166(11):990-8. doi: 10.1001/archpediatrics.2012.1023.
(7) Procedural Sedation and Analgesia in Children: Perspectives from
Paediatric Emergency Physicians [Full Text PDF]. Proceedings of Singapore Healthcare: Volume 19, Number 2, 2010
(8) A Medical Crisis Management Simulation Activity for Pediatric Dental Residents and Assistants [PubMed Abstract] [Full Text HTML] [Full Text PDF]. J Dent Educ. 2011 Jun;75(6):782-90.
(9) How safe is deep sedation or general anesthesia while providing dental care? [PubMed Abstract]. J Am Dent Assoc. 2015 Sep;146(9):705-8. doi: 10.1016/j.adaj.2015.04.005.
(10) Trends in death associated with pediatric dental sedation and general anesthesia [PubMed Abstract] [Full Text HTML] [Full Text PDF]. Paediatr Anaesth. 2013 Aug;23(8):741-6. doi: 10.1111/pan.12210. Epub 2013 Jun 14.
(11) Episode 76 Pediatric Procedural Sedation [Link is to the podcast and show notes] Feb 2016 from Emergency Medicine Cases.
(12) Sim Case Series: Procedural Sedation [Link is to the show notes] December 12th, 2013 from Academic Life In Emergency Medicine.
(13) ALiEMU CAPSULES Module 5: Procedural Sedation & Analgesia in the ED [Link is to the show notes] February 10th, 2016 from Academic Life In Emergency Medicine.
(14) Sedation Provider Course 2009 from The Society For Pediatric Sedation
(15) FDA Drug Safety Communication: FDA review results in new warnings about using general anesthetics and sedation drugs in young children and pregnant women 12-20-2016 from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
(14) FDA Drug Safety Communication: FDA approves label changes for use of general anesthetic and sedation drugs in young children 4-27-2017 from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
(15) Interprofessional and interdisciplinary simulation-based training leads to safe sedation procedures in the emergency department [PubMed Abstract] [Full Text HTML] [Full Text PDF]. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 2016 Aug 2;24:97. doi: 10.1186/s13049-016-0291-7.