Intravenous access is a critical necessity in life-threatening pediatric emergencies. And often in such emergencies timely infant or pediatric IV access is difficult or impossible.
And that is why all pediatricians (family doctors, EMs, NPs, etc) must be skilled in the placement of intraosseous access.
Over the last few months I have been carefully reviewing the recognition and treatment of pediatric shock.
And vascular access is the critical life saving skill in pediatric shock. Below are some my posts in Resources on intraosseous access.
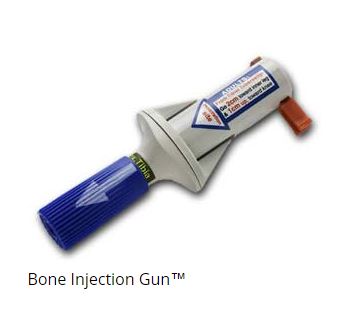
There are basically four different devices available for intraosseous access. There are two manual insertion needles: the Cook IO and the Jamshidi IO. And there are two semi-automatic devices: the EZ-IO and the Bone Injection Gun.
In Reference (1) in Resources, the four devices are discussed.
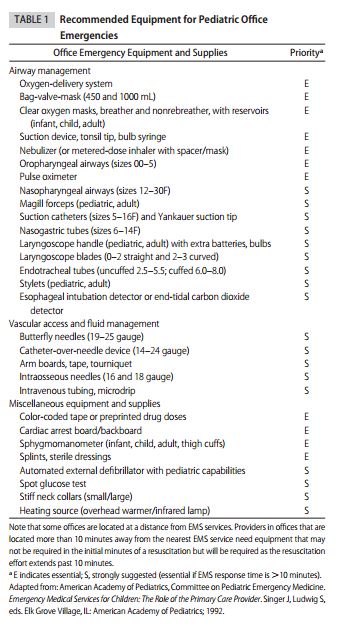
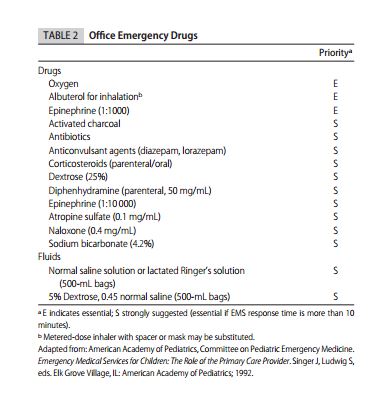
It seems to me that one of the manual needles or the Bone Injection Gun would be most practical for the pediatric office or urgent care office. The American Academy of Pediatrics has made clear suggestions for emergency equipment and medicines for the pediatric office [See Reference (6) – I have included Tables 1 and 2 following Ref (6)]
Resources:
(1) Intraosseous Devices for the Tactical Medic
Nov 12, 2009 from EMS1.com
(2) Intraosseous access Reviewed and revised 10 June 2015 from Life In The Fast Lane
(3) Practicing Newborn Vascular Access With Liz, Newborn Pediatric Transport Nurse Of St. Vincent Hospital – Posted on May 15, 2016 by Tom Wade MD
(4) Intraosseous Access – A Critical Skill For ACLS, and PALS
Posted on May 12, 2016 by Tom Wade MD
(5) Pediatric Intraosseous Access Updated: Feb 13, 2014 from emedicine.medscape.com
(6) Preparation for Emergencies in the Offices of Pediatricians and Pediatric Primary Care Providers (Full Text HTML) (Full Text PDF). Pediatrics. 2007;120(1):200–212. Reaffirmed June 2011.