In this post I link to and excerpt from Emergency Medicine Cases‘ ECG Cases 5: Cardiac Syncope. Written by Jesse McLaren; Peer Reviewed and edited by Anton Helman. January 2020
All that follows is from Dr. McLaren’s outstanding post.
In this ECG Cases blog we look at seven patients with cardiac syncope, and a systematic approach to ECG interpretation…
Cardiac syncope
The 2018 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and management of syncope classifies syncope as reflex (vasovagal, situational or carotid sinus), orthostatic (drug-induced, volume depletion, or autonomic), or cardiac. The latter group can be caused by
- arrhythmia
- bradycardia: sinus or AV conduction disease
- tachycardia: supraventricular or ventricular
- structural
- tamponade
- ACS
- aortic stenosis
- hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM)
- cardiac mass
- prosthetic valve dysfunction
- cardiopulmonary
- PE
- aortic dissection
- pulmonary hypertension
High risk features on history include: syncope with exertion or while supine, preceded by palpitations, family history of sudden death at a young age, or history of heart disease. Fore more on syncope, check out EM cases episode 25: pediatric syncope and adult syncope.
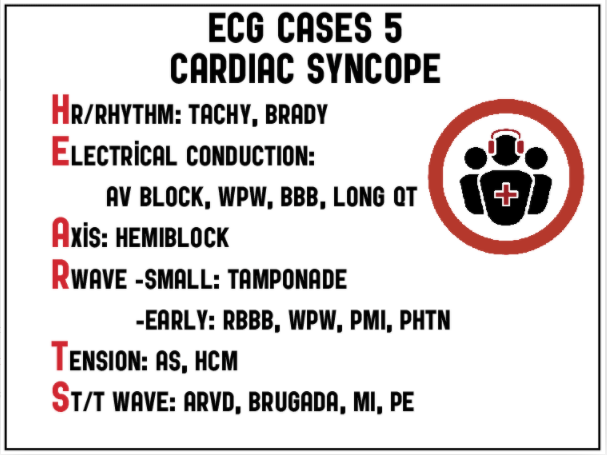
There are many different mnemonics for ECG findings in cardiac syncope, but the same systematic approach to any ECG interpretation will identify them. Just follow the HEARTS.
- Heart rate/rhythm
- tachy
- brady
- Electrical conduction
- PR long (AV block) or short+delta (WPW)
- QRS wide: BBB
- QT prolongation
- Axis
- right: PHTN, PE, LPFB
- left: LAFB
- R wave size/progression
- early R wave: RBBB, WPW type A, posterior MI, pulmonary hypertension
- late R wave: cardiomyopathy
- high voltages: hypertrophy
- low voltages: pericardial effusion
- Tension (hypertrophy)
- aortic stenosis
- HCM
- ST/T wave changes
- inherited: ARVD, Brugada
- ischemic: ACS, PE, dissection
In this ECG Cases blog we look at seven patients with cardiac syncope, and a systematic approach to ECG interpretation…
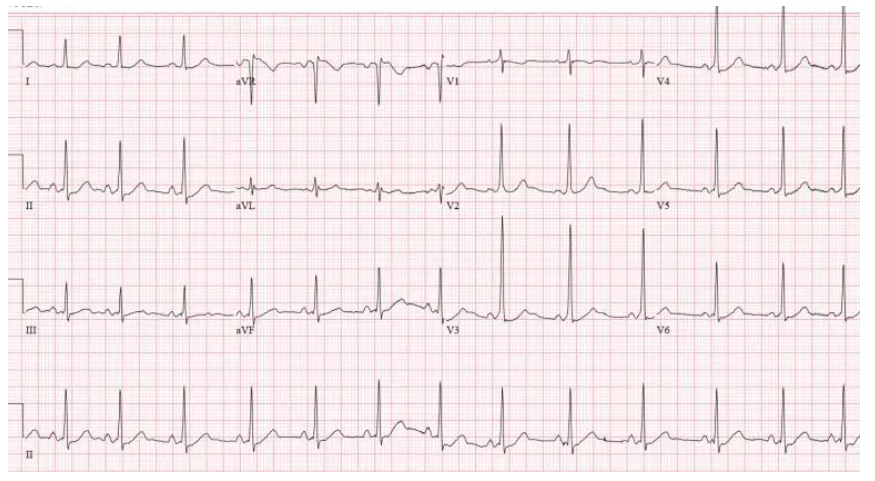
Case 1: 20yo previously well with half an hour of palpitations and presyncope, resolved
Case 1: WPW
- HR/rhythm: NSR.
- Electrical conduction: short PR with delta wave in precordial leads.
- Axis: normal.
- R wave: early progression.
- Tension: none.
- ST/ T changes: mild anterior ST depression, discordant to delta.
Diagnosis: WPW. Referred for ablatation