In addition to the resource in this post, please review the following related articles:
- Immunopathology and Immunotherapy of Inflammatory Skin Diseases [PubMed Abstract]. Immune Netw. 2022 Feb 14;22(1):e7.
- Tetracycline use in treating osteoarthritis: a systematic review [PubMed Abstract]. Inflamm Res. 2021 Mar;70(3):249-259.
- A Brief look at antitumor effects of doxycycline in the treatment of colorectal cancer and combination therapies [PubMed Abstract]. Eur J Pharmacol. 2022 Feb 5;916:174593.
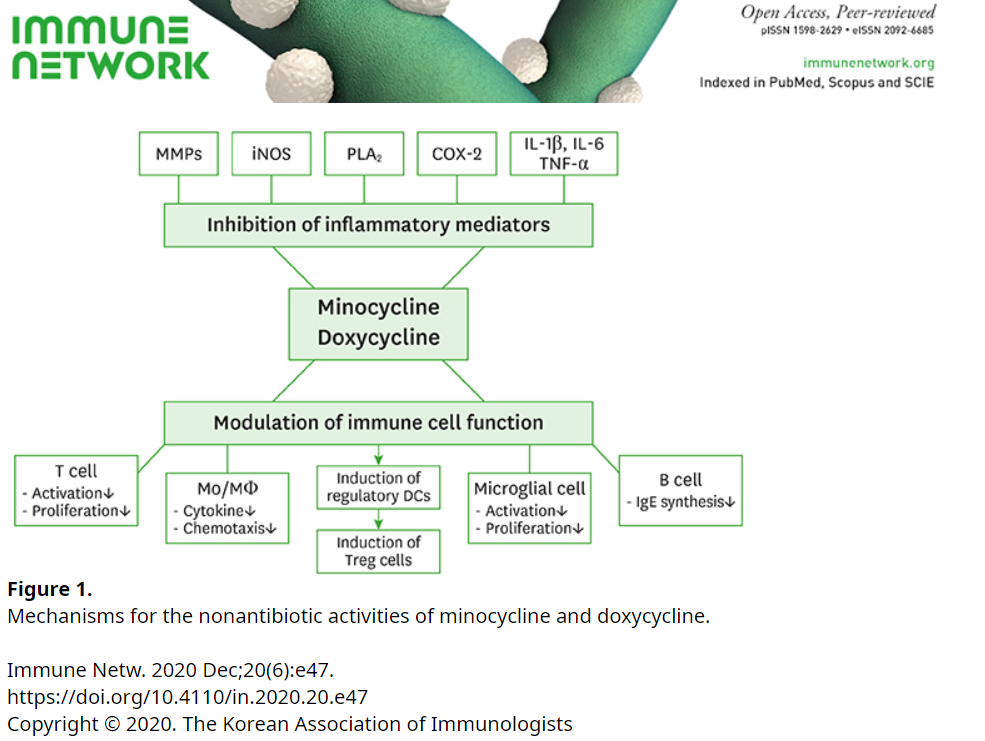
In this post, I link to and excerpt from Immunotherapy of Autoimmune Diseases with Nonantibiotic Properties of Tetracyclines [PubMed Abstract] [Full-Text HTML] [Full-Text PDF]. Immune Netw. 2020 Dec 21;20(6):e47.
There are 37 similar articles in PubMed Central.
All that follows is from the above resource.
Abstract
Tetracyclines, which have long been used as broad-spectrum antibiotics, also exhibit a variety of nonantibiotic activities including anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties. Tetracyclines bind to the 30S ribosome of the bacteria and inhibit protein synthesis. Unlike antimicrobial activity, the primary molecular target for the nonantibiotic activity of tetracycline remains to be clarified. Nonetheless, the therapeutic efficacies of tetracyclines, particularly minocycline and doxycycline, have been demonstrated in various animal models of autoimmune disorders, such as multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and asthma. In this study, we summarized the anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory activities of tetracyclines, focusing on the mechanisms underlying these activities. In addition, we highlighted the on-going or completed clinical trials with reported outcomes.
Keywords: Anti-inflammatory activity; Autoimmune disease; Clinical trial; Doxycycline; Immunomodulatory activity; Minocycline.