In this post I review Vasculitis starting with an exellent slide show from Medscape.
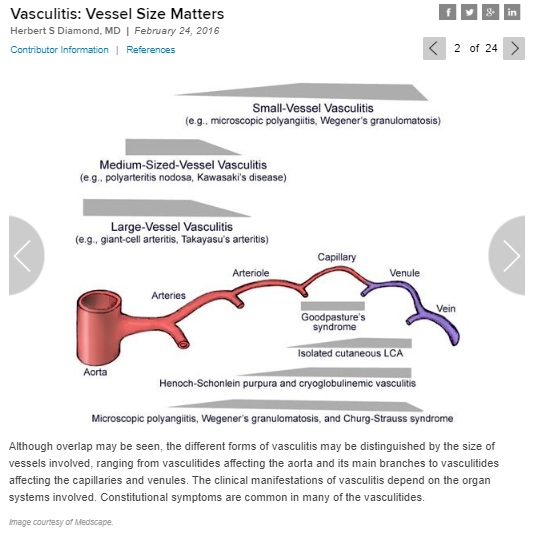
Vasculitis: Vessel Size Matters
Herbert S Diamond, MD | February 24, 2016 from Medscape. The slide show consists of 24 illustration, each of which has its own paragraph of related clinical information.
Here are excerpts from the above:
From the above illustration [I’m repeating it for emphasis because it is so important]:
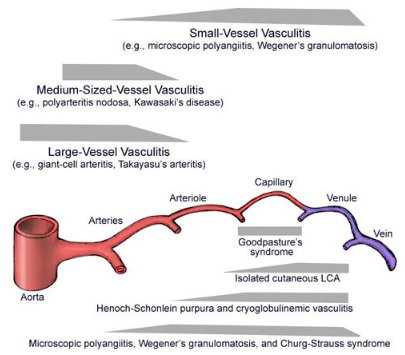
Although overlap may be seen, the different forms of vasculitis may be distinguished by the size of the vessels involved, ranging from the vasculitides affecting the aorta and its main branches to vasculitides affecting the capillaries and venules. The clinical manifestations of vasculitis depend on the organ systems involved. Constitutional symtoms are common in many of the vasculitides.
And here are links to more detailed articles from Medscape on the above vasculitides:
- Small Vessel Vasculitis
- Medium Sized Vasculitis
- Large Vessel Vasculitis
- Goodpasture’s Syndrome
- Isolated Cutaneous LCA – Leukocytoclastic Vasculitis
- Henoch-Schonlein Purpura and Cryoglobunemic Vasculitis [start here]
Can’t upload this slide. Will create a table with the information. Will type in the clinical information.
Recommended Investigation By Suspected Diagnosis Suspected Diagnosis Targeted Study Takayatsu Arteritis CT/ MR/Conventional Angiography of Aorta And Main Branches Primary Angiitis of the CNS MR Angiography of the Head Polyarteritis Nodosa Conventional Angiography Giant Cell Arteritis Temporal Artery Biopsy ANCA-Positive Vasculitidis Sinus, Renal, Lung, and/or Skin Biopsy Henoch-Schonlein Purpura Skin and/or Renal Biopsy Primary Angiitis of the CNS CNS Lesion Biopsy Polyarteritis Nodosa Skin Biopsy Angiography is used to assess for diagnosis of large or medium sized vessels. Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is diagnostic of large or medium-sized vessel primary angiitis of the central nervous system (PACNS); patients with suspected small vessel angiography negative PACNS may require tissue biopsy. Findings in PAN include “beading” of vessels caused by alternating areas of narrowing and dilatation. Histopathologic patterns of vessel inflammation include lymphocytic/giant cell mediated large vessel vasculitis (eg, giaant cell arteritis); necrotizing vasculitis (eg, PAN or Kawasaki disease); antibody-mediated small vessel vasculitis (ie, anca-positive vasculitides); and antibody (IgA) deposition vasculitis (Henoch-Schonlein purpura).