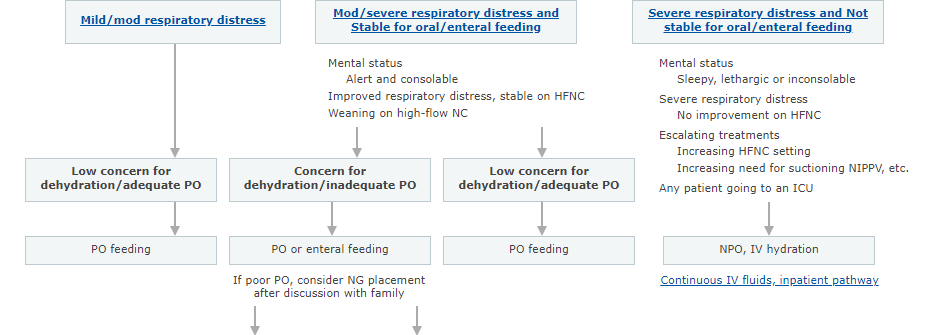
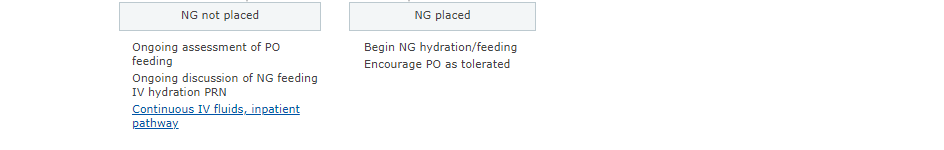
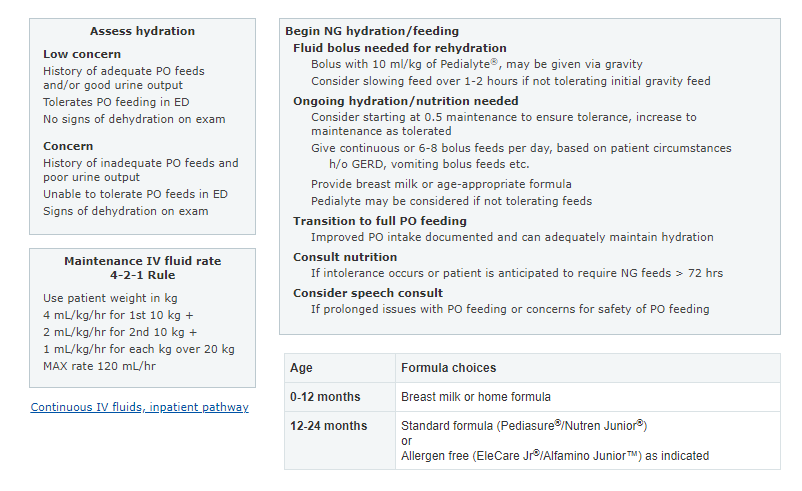
In this post I link to and display a PNG of the Emergency Department and Inpatient Clinical Pathway for Oral or Enteral Feeding in Children with Bronchiolitis [Link is to the interactive web page chart*] from the Children’s Hospital Of Philadelphia.
*Note to myself and my readers: Go to the interactive chart link above and review the pathway there. Also review all the live links on the pathway as, taken together, they provide a great guidance on bronchiolitis, use of NG tubes, and pediatric fluid management.
I will be including a number of the above direct links as posts on my blog. Doing so makes it easier for me to quickly find and review the resource using my blog’s search function.
I will list the posts here when they are added.
Related PathwaysRelated Video
Learn More
- Quality Improvement Initiative to Increase the Use of Nasogastric Hydration in Infants With Bronchiolitis
- Oral Nutrition in Children With Bronchiolitis on High-Flow Nasal Cannula Is Well Tolerated
- Enteral Hydration in High-Flow Therapy for Infants with Bronchiolitis: Secondary Analysis of a Randomised Trial
I’ve included this PNG of the pathway below for quick review. But the reader of the post should actually review the Pathway on the CHOP web page because of all the great related live links.
Patient with Mod/Severe Respiratory Distress and Stable for Oral/Enteral Feeding
- Mental Status: Alert, consolable
- Improved respiratory status and stable on high flow NC
- Weaning on high flow NC
Baseline Assessment
The highest rating in any of the categories below determines the patient’s starting position on the pathway. A severe rating in any category indicates a starting position in the Severe classification. All Moderate assessments, or a mix of Mild and Moderate would indicate a starting position in the Moderate classification. When in doubt, err on the side of classifying a patient as more severe.
Mild (0) Moderate (1) Severe (2) RR < 3 months 30-60 61-80 > 80 3 – < 12 months 25-50 51-70 > 70 1y – 2y 20-40 41-60 > 60 WOB None or mild Intercostal retractions Nasal flaring, grunting, head bobbing Mental Status Baseline Fussy or anxious Lethargic or inconsolable Oxygen Requirement None* Any Any Suctioning Bulb Wall/Bulb Wall *Any need for supplemental oxygen precludes Mild classification
Patient with Bronchiolitis Who Is Allowed Oral/Enteral Feeding
This pathway should be used to guide the care of healthy patients < 24 months of age in the Emergency Department who are going to be admitted or already admitted to any inpatient general pediatric service with a clinical presentation consistent with the diagnosis of bronchiolitis.
Consider excluding any patient with the following:
- Distress
- NPO, potential need for care escalation
- Concern for possible severe sepsis
- Risk for feeding intolerance
- IV fluids for shock
- Persistent emesis, severe GERD, aspiration risk
- Craniofacial abnormalities that will make placing an NG tube difficult
- Critical airway