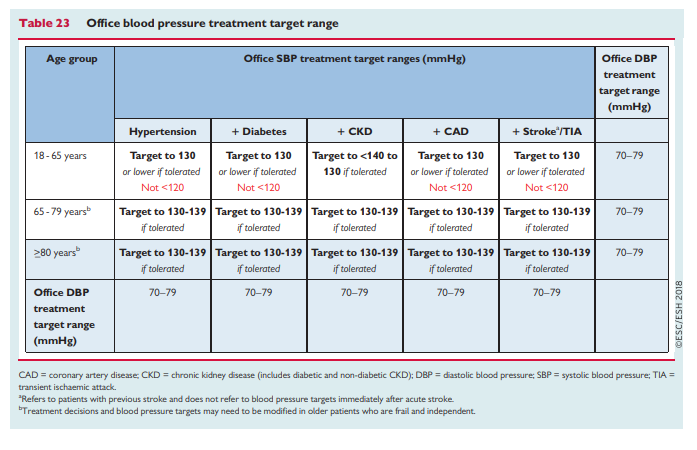
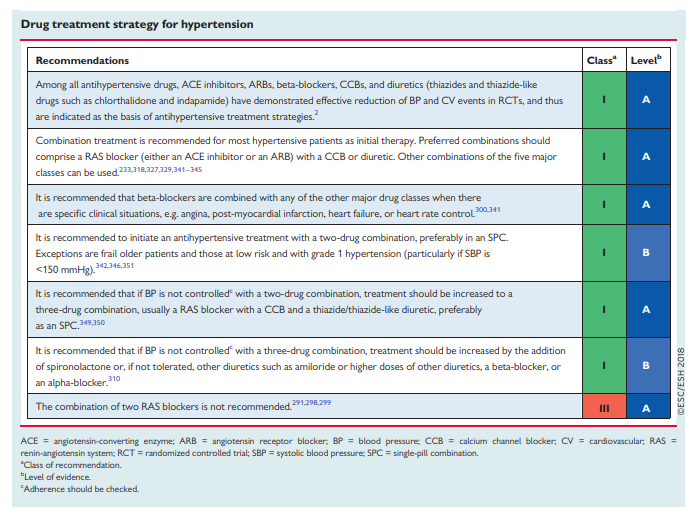
I’ve divided these posts, my study notes on the European high blood pressure guidelines, into several parts for ease of my review:
- Here is the link to Diagnosis of Hypertension-Part 1 Of Links To And Excerpts From The 2018 European Guidelines For The Management Of Hypertension
Posted on November 10, 2019 by Tom Wade MD - Here is the link to Treatment of Hypertension-Part 2 Of Links To And Excerpts From The 2018 European Guidelines For The Management Of Hypertension
Posted on November 15, 2019 by Tom Wade MD - This post is The Drug Treatment Algorithm For Hypertension – Part 3 Of Links To And Excerpts From The 2018 European Guidelines For The Management Of Hypertension
Posted on November 16, 2019 by Tom Wade MD - Here is the link to Hypertension In Specific Circumstances – Part 4 Of Links To And Excerpts From The 2018 European Guidelines For The Management Of Hypertension
Posted on November 16, 2019 by Tom Wade MD
The following are excerpts from The Drug Treatment Algorithm For Hypertension section from the 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension [PubMed Abstract] [Full Text HTML] [Full Text PDF]. Eur Heart J. 2018 Sep 1;39(33):3021-3104. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy339:
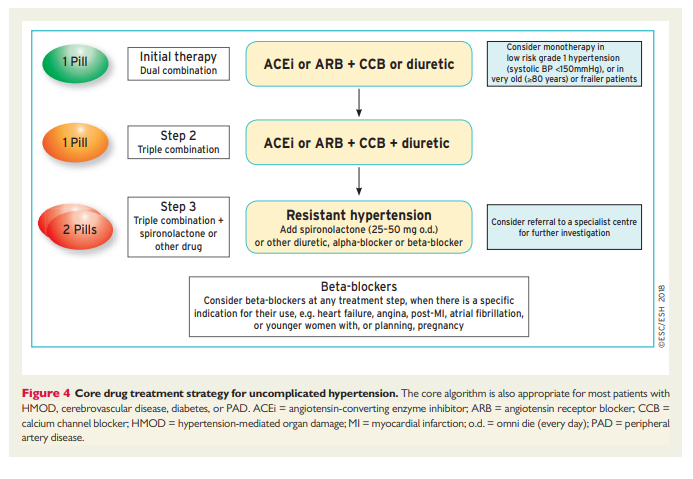
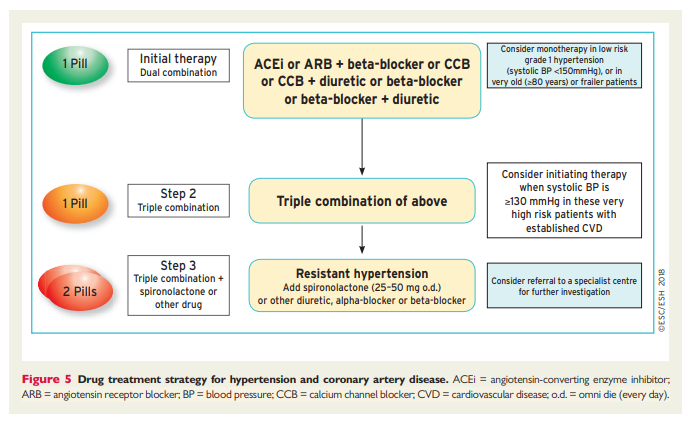
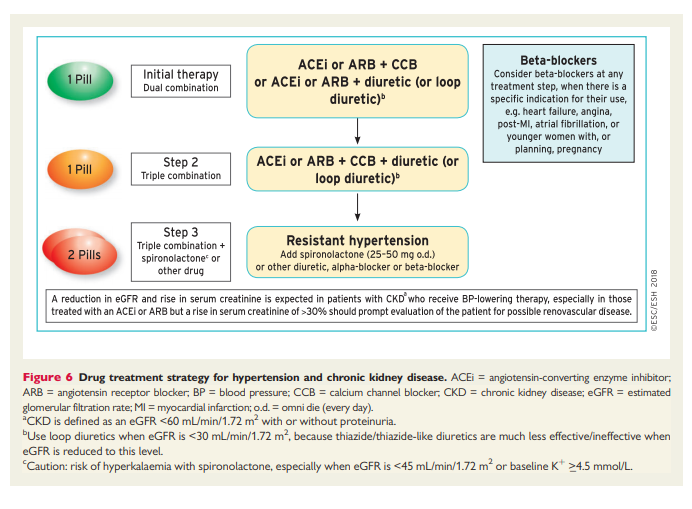
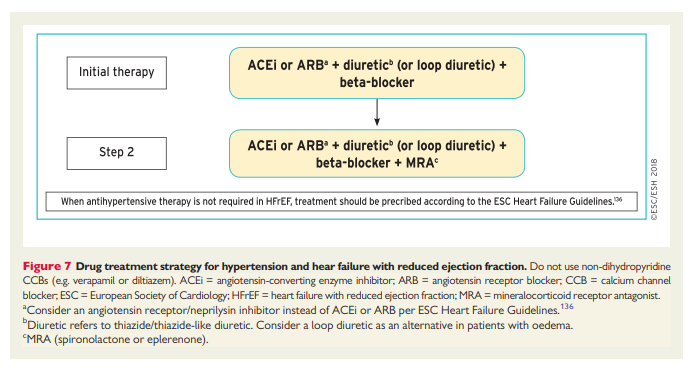
7.5.3 The drug treatment algorithm for hypertension
Reflecting on the evidence above, and recognizing the urgent need to address the factors contributing to the poor control of BP in treated hypertensive patients (see section 7.5.1), this drug treatment algorithm has been developed to provide a simple and pragmatic treatment recommendation for the treatment of hypertension, based on a few key recommendations:
(1) The initiation of treatment in most patients with an SPC comprising two drugs, to improve the speed, efficiency, and predictability of BP control.
(2) Preferred two-drug combinations are a RAS blocker with a CCB or a diuretic. A beta-blocker in combination with a diuretic or any drug from the other major classes is an alternative when there is a specific indication for a beta-blocker, e.g. angina, post-myocardial infarction, heart failure, or heart rate control.
(3) Use monotherapy for low-risk patients with stage 1 hypertension whose SBP is <150 mmHg, very high-risk patients with high–normal BP, or frail older patients.
(4) The use of a three-drug SPC comprising a RAS blocker, a CCB, and a diuretic if BP is not controlled by a two-drug SPC.
(5) The addition of spironolactone for the treatment of resistant hypertension, unless contraindicated (see section 8.1.4).
(6) The use of other classes of antihypertensive drugs in the rare circumstances in which BP is not controlled by the above treatments.
(7) Information on availability and recommended doses of individual drugs, as well as SPCs and free combinations, can be found in national formularies.
And now go on to
Hypertension In Specific Circumstances – Part 4 Of Links To And Excerpts From The 2018 European Guidelines For The Management Of Hypertension
Posted on November 16, 2019 by Tom Wade MD
Resources:
(1) 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension [PubMed Abstract] [Full Text HTML] [Full Text PDF]. Eur Heart J. 2018 Sep 1;39(33):3021-3104. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy339.
(2) 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. [PubMed Citation] [Full Text PDF]. Hypertension. 2018 Jun;71(6):1269-1324. doi: 10.1161/HYP.0000000000000066. Epub 2017 Nov 13.
(3) Screening for Endocrine Hypertension: An Endocrine Society Scientific Statement [PubMed Abstract] [Full Text HTML] [Full Text PDF]. Endocrine Reviews, Volume 38, Issue 2, 1 April 2017, Pages 103–122
(4) 2016 European Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice [PubMed Abstract] [Full Text HTML] [Full Text PDF]. Atherosclerosis. 2016 Sep;252:207-274. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2016.05.037.
(5) “HOW TO CHECK A HOME BLOOD PRESSURE MONITOR FOR ACCURACY” From The American Medical Association
Posted on November 14, 2019 by Tom Wade MD