In this post, I link to and excerpt from “Septic Arthritis vs Transient Synovitis” From EM Quick Hits 34 Carr’s Case, Septic Arthritis vs Transient Synovitis, Managing Tracheostomies, Ethylene Glycol Poisoning, Ketamine for Agitation.
Helman, A., Swaminathan, A., Khatib, N., Reid, S., H. Carr, D., Morgenstern J. EM Quick Hits 34 – Carr’s Case, Septic Arthritis vs Transient Synovitis, Managing Tracheostomies, Ethylene Glycol Poisoning, Ketamine for Agitation. Emergency Medicine Cases. November, 2021. https://emergencymedicinecases.com/em-quick-hits-november-2021/. Accessed 12-6-2021.
Topics in this EM Quick Hits podcast
David Carr the mighty return of Carr’s Cases! (00:38)
Sarah Reid on differentiating septic arthritis from transient synovitis in pediatric limp (18:52)
Anand Swaminathan on managing tracheostomy complications in the ED (27:50)
Nour Khatib on rural medicine and ethylene glycol poisoning (37:52)
Justin Morgenstern on RCTs for ketamine in patients with severe agitation (48:17)
All that follows is from Sarah Reid on differentiating septic arthritis from transient synovitis in pediatric limp (18:52-27:50)
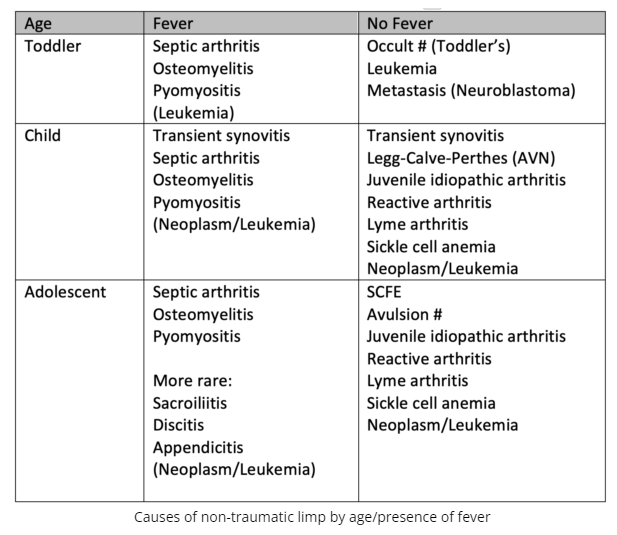
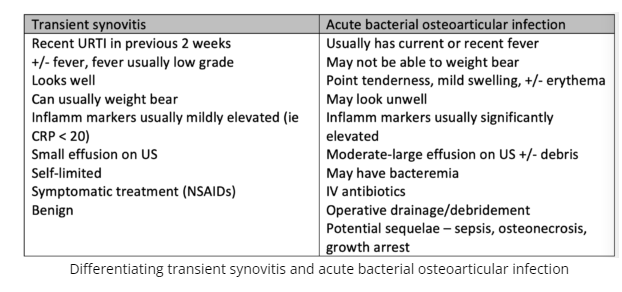
- Age and fever dictate differential for nontraumatic pediatric limp
- Workup to consider:
- Xrays
- CBCD, CRP, blood culture if infection/inflammatory cause suspected to help distinguish between transient synovitis and osteoarticular infection
- US (for effusion, soft tissues) if significant fever and/or elevation of inflammatory markers and/or severe pain
- MRI with gadolinium is the most accurate noninvasive test for osteoarticular infection and should be considered for patients with persistent pain/fever
- Volume of blood matters when obtaining blood for culture and sensitivity which is essential, as hematogenous spread is common in children with osteoarticular infections
References
- https://www.cps.ca/documents/position/osteoarticular-infections-in-children
- Peltola H. and Paakkonen M. Acute Osteomyelitis in Children. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:352-360.
- Tu J, et al. Test characteristics of history, examination and investigations in the evaluation for septic arthritis in the child presenting with acute non-traumatic limp. A systematic review. BMJ Open 2020;10:e038088.