For further information on Antinuclear Antibody Testing, please see:
- Links To And Excerpts From Automated evaluation of ANA under real-life conditions
Posted on October 20, 2020 by Tom Wade MD - Link To And Excerpts From “Antinuclear antibodies: When to test and how to interpret findings” With A Link To The Rheumatologic Review Of Systems
Posted on October 22, 2020 by Tom Wade MD - Links To And Excerpts From Antinuclear antibodies in healthy people and non-rheumatic diseases – diagnostic and clinical implications
Posted on October 22, 2020 by Tom Wade MD
I was asked to review an extensive set of laboratory and imaging evaluations triggered by a low white count.
The patient’s rheumatologist saw the patient several days ago and stated that all her tests were negative and that she did not have a connective tissue disorder.
I simply went over with the patient why the tests were ordered and why they were all normal.
Tests ordered by the patient’s hematologist were antinuclear antibody tests on 8-25-2020 was reported as:
ANA Screen, IFA Positive Normal result is negative
Lab Comment: ANA IFA is a first line screen for detecting up to 150 autoantibodies in various autoimmune diseases. A positive ANA IFA is suggestive of autoimmune disease and reflexes to titer and pattern.
ANA Titer 1:80
ANA Pattern Nuclear, Speckled
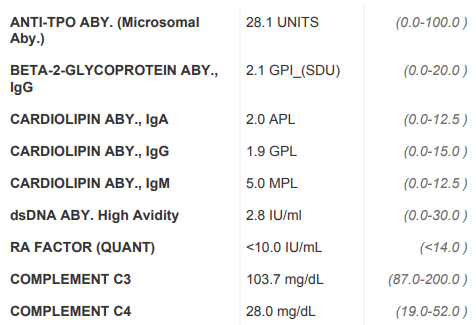
And on 9-30-2020, her rheumatologist ordered the following:
09/30/2020Cardiolipin, antibody, each lg classCompleted
09/30/2020Cardiolipin, antibody, each lg classCompleted
09/30/2020Uric Acid; BloodCompleted
09/30/2020C-Reactive Protein ( Crp )Completed
09/30/2020Comprehensive Metabolic PanelCompleted
09/30/2020Urinalysis /wo Micro RoutineCompleted
09/30/2020ANA (antinuclear Antibodies )Completed
09/30/2020Extractable nuclear antigen, each AntibodyCompleted
09/30/2020Cyclic citrullinated peptide, antibodyCompleted
09/30/2020Cardiolipin, antibody, each lg classCompleted
09/30/2020Microsomal antibodies, eachCompleted
09/30/2020Complement AntigenCompleted
09/30/2020Rheumatoid Factor;qauntitativeCompleted
It is not clear what laboratory the blood was sent to. I will attempt to contact the rheumatologist who ordered the tests below. Then I can ask the lab about the performance characteristics of the ANA ANTIBODY SCREEN QUANT and the other tests that follow.
I assume that the tests that follow below were automated tests of ANA and the subsequent tests reflexed when the ANA was positive.