I just listened to by Beth Garbatelli‘s awesome May 20, 2019 Curbsiders‘ episode #150 HFpEF [Link is to the show notes and podcast] with Dr Clyde Yancy MD:
Best practices update and the future of heart failure with preserved EF
Summary
Update on current best practices and the future of HFpEF (heart failure with preserved ejection fraction) with master cardiologist, Dr Clyde Yancy MD, Chief of Cardiology and Professor of Medicine (Cardiology) and Medical Social Sciences, Northwestern, Feinberg School of Medicine. Topics include: pathophysiology, HFpEF phenotypes, how to interpret a borderline ejection fraction, evidence based therapies, diuretics, and future directions (pulmonary artery monitors, interatrial shunts, ARNI* compounds), and more!
The combination of Sacubitril/valsartan**, sold under the brand name Entresto among others, is a combination drug for use in heart failure developed by Novartis. It consists of the neprilysin inhibitor sacubitril and the angiotensin receptor blocker valsartan, in a 1:1 mixture by molecule count. It is recommended for use as a replacement for an ACE inhibitor or an angiotensin receptor blocker in people with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.[1] [From Wikipedia]
*neprilysn – A Test in Context: Neprilysin: Function, Inhibition, and Biomarker [PubMed Abstract] [Full Text HTML] [Full Text PDF]. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016 Aug 9;68(6):639-653. This post has been cited by 17 articles in PubMed Central.
**sacubitril/valsartan (Rx) [Link is to the drug monograph from Medscape. From the monograph:
[A very important adverse effect of sacubitril/valsartan is] Angioedema***, all patients (0.5%); in black patients (2.4%).
***Angioedema in the emergency department: a practical guide to differential diagnosis and management [PubMed Abstract] [Full Text HTML] [Full Text PDF]. Int J Emerg Med. 2017 Dec;10(1):15.
Time Stamps
- 00:00 Thanks to our producers Sarah Phoebe Roberts, Beth Garbitelli and Justin Berk
- 00:50 Intro and guest bio
- 04:00 Guest one liner, career advice
- 08:20 Ms Diana Stolic has HFpEF. What’s the difference in HFpEF and diastolic dysfunction?
- 11:33 How should we think about borderline ejection fraction?
- 15:24 Pathophysiology and Phenotypes of HFpEF
- 18:57 More on the pathophysiology of HFpEF (nitric oxide, fibrosis, inflammatory signaling)
- 21:00 Are there morbidity and mortality differences for HFpEF versus HFrEF?
- 24:45 What historical factors are most important in HFpEF?
- 27:50 Pulmonary artery monitors for HFpEF
- 29:00 Does Diuretic therapy differ in HFpEF and HFrEF?
- 33:44 Ischemic workup for new HFpEF
- 35:33 Right heart cath for HFpEF
- 36:53 Future of HFpEF
- 41:04 Will ARNI compounds work for HFpEF? What are the current medications for HFpEF?
- 45:20 SGLT2 inhibitors for heart failure
- 46:30 Outro
HFpEF Pearls
The first discrimination point in CHF is preserved vs. reduced ejection fraction.
There are multiple phenotypes of HFpEF and they may have different therapeutic strategies.
The mortality rate of HFpEF is lower than HFrEF, but the morbidity may be worse.
There are no significant differences in physical exam findings between HFpEF and HFrEF.
For new HFpEF, there should be a coronary work-up. This may be initially done with coronary CT rather than catheterization.
New imaging strategies of the LAD may help predict which patients will have HFpEF.
New evidence suggests interatrial shunts may offer symptomatic and mortality benefit.
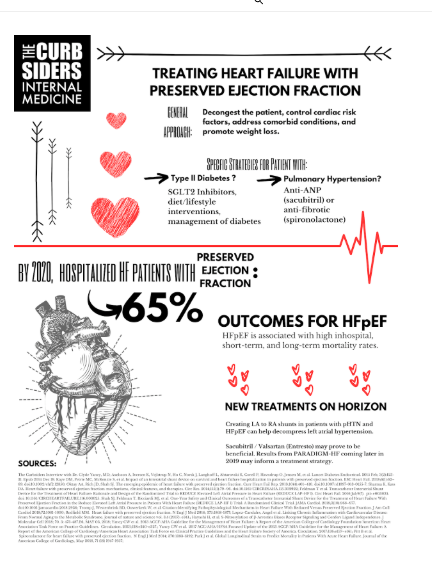
Basic treatment plan should include: diuresis for dyspnea, spironolactone (if elevated proBNP), SGLT2i if diabetes.
Future research is underway to evaluate SGLT2i in non-diabetics and sacubitril/valsartan (an ARNI compound) in HFpEF.
HFpEF Show Notes
Definitions
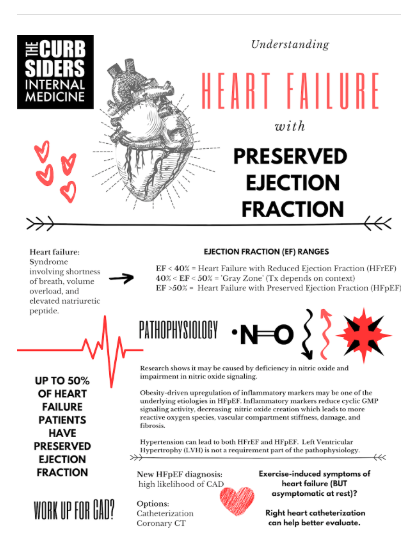
Heart Failure – The syndrome of shortness of breath, volume overload, and elevated natriuretic peptide.
Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) – The first discrimination point in the heart failure syndrome. EF is considered ‘preserved’ if normal (i.e. >50%).
Ejection Fraction: How much blood is emitted with each contraction of the ventricle in comparison to how much blood is in the heart.
Global Longitudinal Strain: Measures the deformation of the myocardium during systole. Less load dependent and more reflective of intrinsic ventricular functioning, contractility.
Diastolic Dysfunction – Specific hemodynamic consequences associated with valvular disease or ischemia.